Blister packaging plays a crucial role in protecting medications from environmental factors such as moisture, light, and air, ensuring their safety, potency, and effectiveness. This packaging method is widely used for tablets, capsules, and suppositories due to its ability to provide reliable protection, ease of use, and extended shelf life.Whether you are new to the industry or looking to refine your packaging knowledge, understanding these essential components is vital to maintaining the integrity and safety of pharmaceutical products.
Blister Packaging Materials
The materials used for blister packaging of pharmaceutical blister packaging machines mainly include plastic sheets, substrate materials, heat-sealing coating materials and substrate printing inks.
(1) Plastic sheet materials
The rigid plastic sheets commonly used for blister packaging of pharmaceutical blister packaging machines mainly include polyvinyl chloride, polyvinylidene chloride and some composite materials. Currently, the most widely used is polyvinyl chloride rigid sheet.
Rigid polyvinyl chloride sheets have good transparency and gloss. Polyvinyl chloride sheets used for pharmaceutical packaging have high requirements for the hygiene of the resin and must use non-toxic polyvinyl chloride resins, non-toxic modifiers and non-toxic heat stabilizers.
Polyvinylidene chloride has a high molecular density, regular structure, high crystallinity, extremely strong gas sealing, excellent moisture resistance, good oil resistance, drug resistance and solvent resistance, and excellent barrier properties to oxygen, water vapor and carbon dioxide in the air. Compared with materials of the same thickness, the barrier property of polyvinylidene chloride to oxygen is 1500 times that of polyethylene, 100 times that of polypropylene, and 100 times that of polyester. It is better than polyethylene in terms of water vapor and oxygen resistance. Moreover, the sealing performance, impact strength, tensile strength and durability of polyvinylidene chloride materials can meet the special requirements of blister packaging such as medicines. Therefore, polyvinylidene chloride is one of the development directions of blister packaging materials in the future. Composite plastic sheets for drug blister packaging include PVC/PVDC/PE, PVDC/OPP/PE, PVC/PE, etc. For drugs that require barrier properties and light protection, materials composited with plastic sheets and aluminum foil can be used, such as PET/aluminum foil/PP, PET/aluminum foil/PE composite materials.
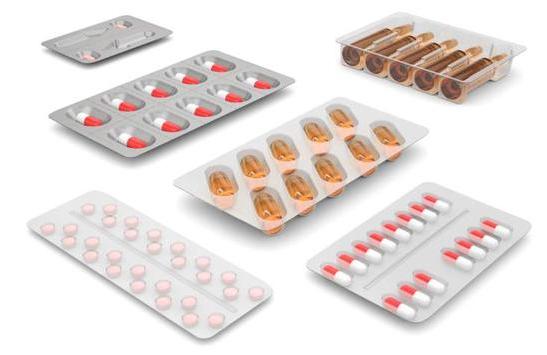
(2) Substrate material
The substrate for blister packaging of tablets and capsules often uses coated aluminum foil. The aluminum foil is made of 99% pure electrolytic aluminum and is made by calendering. The aluminum foil has a highly dense metal crystal structure, is non-toxic and odorless, has excellent light-shielding properties, has extremely high moisture resistance, gas barrier properties and taste retention properties, and can most effectively protect the packaged items. It is widely used in drug blister packaging. The surface of the substrate should be neat and glossy, with good printability, and can be firmly coated with a heat-sealing coating to ensure that after the heat-sealing coating is melted, the substrate and the blister can be tightly combined together.
(3) Heat-seal coating materials
The heat-seal coating should be compatible with the substrate and the blister, and the heat-seal temperature should be relatively low so that it can be heat-sealed quickly without damaging the blister film. At present, the heat-seal coating materials used in pharmaceutical blister packaging are mainly divided into single-component adhesives and two-component adhesives. Single-component adhesives are mainly composed of natural rubber or synthetic rubber, nitrate cotton, and acrylic esters. They are non-drying and hot-soluble and have a certain bonding strength. Two-component adhesives are mainly polyurethane adhesives, which have good resistance to high and low temperatures, resistance to medium erosion, high adhesion, etc., and can bond multiple materials at the same time. It has been widely used in adhesives for substrate aluminum foil coating and in the composite process of various plastic films. Other commonly used heat-seal coating materials include solvent-resistant vinyl resins and water-resistant acrylic resins, both of which have good gloss, transparency and heat-sealing properties.
(4) Substrate printing ink
Considering the printing process of aluminum foil substrate for pharmaceutical blister packaging and the special requirements of pharmaceutical packaging, its printing ink must have good adhesion to aluminum foil, the printed text and pattern must be firm and clear, the solvent release must be good, the heat resistance must be good, the friction resistance must be excellent, the gloss must be good, the pigment must be non-toxic, and it must not pollute the packaged medicines. The practical viscosity must meet the process requirements of aluminum foil printing.
At present, the ink used for aluminum foil substrate printing is mainly divided into two categories: the first category is alcohol-soluble polyamide ink. Since polyamide resin has good adhesion to various substances, it is especially suitable for printing polyolefin films, plus good dispersibility, good gloss and softness, good wear resistance, good solvent release and printing properties, so it is often used to prepare special plastic films. LDPE, CPP, OPP and other surface printing gravure printing inks after treatment. This kind of ink has the characteristics of good gloss, wide application, anti-adhesion, easy drying, etc., and is also used for printing aluminum foil substrate for pharmaceutical blister packaging. The second type of ink is a special aluminum foil ink with vinyl chloride vinyl acetate copolymer resin and acrylate resin as the main component. It is characterized by bright color, high concentration, strong adhesion to aluminum foil, good transparency, excellent reproducibility of the metallic luster of aluminum foil, and by adjusting the composition of its mixed solvent to meet the needs of aluminum foil surface printing, it will be more used in substrate aluminum foil printing.
Type of blister packaging equipment
Blister packaging machines are divided into two types according to the degree of automation: semi-automatic packaging machines, automatic packaging machines and fully automatic production lines. The packaging of drugs (tablets, capsules and suppositories, etc.) mainly uses automatic packaging production lines, also known as PTP (Press Through Pack) automatic packaging lines. There are two types: horizontal and vertical. Generally, a multi-column structure is adopted, with high productivity and good packaging quality. It is equipped with a detection device and a waste rejection mechanism, which can connect the printing, distribution of instructions and boxing processes to the production line. It is a typical automatic packaging production line with complete packaging functions.
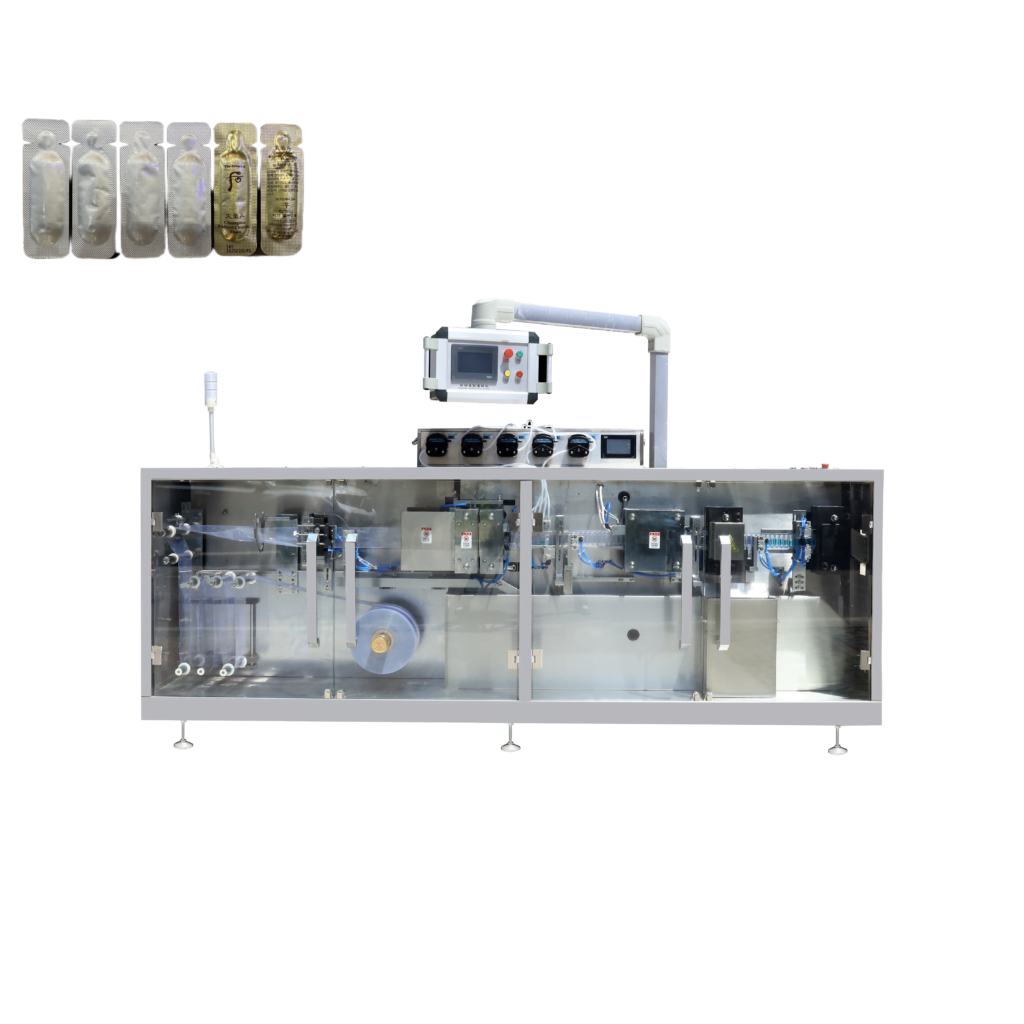
Composition of blister packaging equipment
Pharmaceutical blister packaging machines are basically the same as blister packaging equipment for other products, and are mainly composed of the following parts:
① Heating part. The heating device is used to heat the plastic sheet to soften it for easy molding.
According to the different contact methods between the heater and the thin sheet, there are two heating methods: direct heating and indirect heating. Direct heating is to make the thin sheet contact with the heater, and the heating speed is fast, but uneven, which is suitable for heating thinner materials; indirect heating is to use radiant heat to heat close to the thin sheet, which is thorough and uniform, but the speed is slow, and it is suitable for both thick and thin materials.
According to the different heat sources of the heater, the heating methods are hot air flow heating and thermal radiation heating. Hot air flow heating uses high-temperature hot air flow to directly spray the surface of the heated plastic thin sheet. This method has low heating efficiency and is not uniform enough; thermal radiation heating uses the light radiation and high temperature generated by the far-infrared heater to heat the thin sheet of the bend material, which has high heating efficiency and uniformity.
② Molding part. The molding part can be divided into two methods: dental molding and vacuum molding. Compression molding is to use compressed air to blow the softened thin sheet to the mold so that it is close to the inner wall of the mold to form a blister. The mold adopts a flat plate shape, which is generally intermittently conveyed or continuously conveyed. It has good molding quality and is suitable for both deep and shallow blisters. Vacuum molding is to absorb the softened thin sheet to the inner wall of the mold to form a blister by vacuuming. The mold mostly adopts a roller shape for continuous conveying. Because the suction force generated by the vacuum is limited, and the angle at which the blister leaves the roller after forming is limited, it is only suitable for shallow blisters and thinner materials.
③ Filling device. The drug is quantitatively filled into the formed blister, and a multi-row quantitative automatic filling device is mostly used.
④ Heat sealing device. The aluminum foil substrate material used for covering is sealed on the blister. There are two types: flat plate and roller. The flat plate type is used for intermittent conveying; the roller type is used for continuous conveying.
Production process of blister packaging
The basic process of blister packaging is: heating of plastic sheet, film forming, and because the production batch of blister packaging of medicines by blister packaging machine is large, the varieties are relatively fixed, and safety and hygiene are required, it is advisable to use an automated blister packaging machine packaging line for production. During automated operation, in addition to completing the packaging process, printing, installation of instructions, boxing and other processes can also be connected to the packaging line to form a fully automated blister packaging production line. The production process is as follows:
Filling products, covering substrates, heat sealing, trimming and trimming.
(a) The roll of plastic film is unrolled and conveyed forward;
(b) The film is heated and softened, and then formed into blisters by compression molding (using compressed air) or suction molding (using vacuum) in the mold;
(c) The product is filled with the automatic feeding mechanism;
(d) The quality of blister molding and filling is detected. In the automatic production line, photoelectric detectors are often used. When unqualified products are found, the defective signal is sent to the memory device. After the punching process is completed, the defective products are automatically removed;
(e) The roll substrate material is covered on the filled blister;
(f) The blister and substrate are sealed together with a plate or roller heat sealer;
(g) The batch number and date are printed on the back of the substrate;
(h) Punch into individual packaging units. After the punching process is completed, the defective rejection device removes the defective products according to the signal stored in the memory device.
(j) The instructions and boxes are installed to become sales packages.
Conclusion
Pharmaceutical blister packaging is a vital process ensuring the safety, protection, and integrity of medicines. By using high-quality materials such as polyvinyl chloride, polyvinylidene chloride, and aluminum foil, along with efficient automated equipment, the blister packaging process not only meets the stringent hygiene and safety standards but also provides enhanced barrier protection against moisture, light, and air. The production process, from heating and forming plastic sheets to filling and heat sealing, guarantees a reliable and secure packaging solution for pharmaceutical products. As the industry continues to evolve, the development of advanced materials and packaging technologies will further improve the efficiency and sustainability of blister packaging, making it an indispensable choice in the pharmaceutical sector.