Introduction
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, efficiency and precision are paramount. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) have become the cornerstone of modern automation, driving productivity across various industries. But what exactly is a PLC control system, and how can it revolutionize your operations? This guide delves into the intricacies of PLC control systems, the case of automatic packing machines, answering frequently asked questions, highlighting their benefits, and offering actionable insights to maximize their potential.

Understanding PLC Control Systems
What is a PLC Control System?
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is an industrial digital computer designed to manage manufacturing processes or robotic devices. PLCs monitor inputs, make decisions based on programmed logic, and control outputs to automate processes. They are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, food and beverage, and energy for tasks ranging from simple machine control to complex automation.
How Does a PLC Control System Work?
PLCs operate by receiving input signals from sensors and devices, processing these signals according to a pre-programmed logic, and sending output commands to control machinery and processes. The system is highly customizable, allowing users to program the PLC to perform specific functions based on their unique operational needs.
Why Are PLC Control Systems Essential in Automation?
PLC control systems offer unparalleled reliability, flexibility, and scalability, making them essential in modern automation. They can handle a wide range of tasks, from simple switching operations to complex process controls, all while ensuring consistent performance. The ability to easily modify and expand the system as operational requirements evolve is a significant advantage over traditional control systems.
Benefits of Implementing a PLC Control System
1. Increased Efficiency
PLCs streamline operations by automating repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and minimizing downtime. This leads to increased productivity and cost savings.
2. Enhanced Precision
With precise control over processes, PLCs ensure consistent quality and output, crucial for industries where precision is key, such as pharmaceuticals and electronics.
3. Flexibility and Scalability
PLC systems can be easily reprogrammed and scaled to accommodate changing production needs, making them a future-proof investment.
4. Robust Performance
Designed to withstand harsh industrial environments, PLCs are known for their durability and reliability, ensuring uninterrupted operations.
5. Cost-Effectiveness
Although the initial investment in a PLC system may be high, the long-term savings in labour, maintenance, and operational efficiency make it a cost-effective solution.
Case Studies of Automatic Packing Machines
Automatic packing machines have been widely adopted across various industries to improve efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. Here are a few case studies showcasing the benefits of using PLCs in automatic packing machines:
Automatic Packing of Powder Products
A PLC-controlled automatic packing machine was developed to pack various-sized products, reducing total project costs.
The machine uses sensors to detect products in a single line and packs them based on the PLC program. Key features include:
- Ability to handle products of different sizes
- Reduced labor costs and increased efficiency
- Improved accuracy and consistency in packing
Automatic Food Packaging
An automatic food packaging machine was designed using a PLC to increase the speed, accuracy, and effectiveness of the packaging process.
The system includes:
- Vibrator to shake objects into a hopper
- Load cell to measure object weight
- PLC to control the entire process
- HMI for user interaction
This fully automated system eliminates the need for manual labor, decreases product time, and increases output compared to traditional manual systems.
Automatic Plastic Pouch Packing
A review paper examined the process and packing principles, techniques, methods, and state-of-the-art technologies used in automatic plastic pouch packing machines
Pouch packing machines automate the packaging of products in plastic pouches, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.
Automatic Metal Separation and Packaging
A PLC-based system was developed to automatically separate metal objects and package them.
The system provides high accuracy and flexibility, demonstrating the versatility of PLCs in automating complex packaging processes.These case studies highlight how PLCs enable the development of efficient, flexible, and cost-effective automatic packing machines across various industries.
By incorporating sensors, actuators, and advanced control algorithms, PLCs optimize packaging processes, reduce errors, and improve overall productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions About PLC Control Systems
What Industries Benefit Most from PLC Control Systems?
PLCs are versatile and can be used across various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: For assembly lines, robotic controls, and monitoring systems.
- Automotive: To manage production lines and ensure quality control.
- Food and Beverage: For process control, packaging, and quality assurance.
- Energy: To automate power generation, distribution, and grid management.
How Does a PLC Compare to a DCS (Distributed Control System)?
While both PLCs and DCS are used in industrial automation, they serve different purposes. PLCs are ideal for discrete control systems that require fast response times, such as assembly lines. DCS, on the other hand, is better suited for continuous processes like chemical production, where the focus is on managing complex operations over large areas.
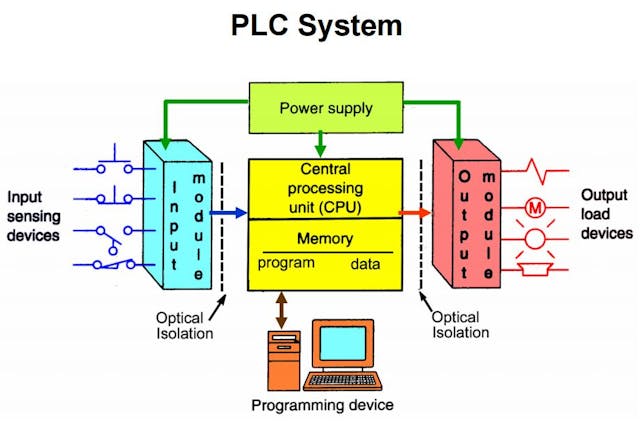
What Are the Key Components of a PLC System?
PLCs consist of several key components:
- Processor Unit (CPU): The brain of the PLC, responsible for executing control programs and processing input signals.
- Memory Unit: Stores the program instructions and data from input devices.
- Input/Output Interface: Facilitates communication between the PLC and external devices, allowing it to receive data from sensors and send commands to actuators.
- Power Supply: Converts AC voltage to DC to power the PLC.
- Communications Interface: Enables data exchange with other PLCs or systems over networks.
PLCs can be designed in two main configurations:
- Modular PLCs: Composed of multiple modules that can be customized for specific applications, allowing for scalability and flexibility.
- Compact PLCs: All components are housed in a single unit, suitable for smaller applications.
How Do You Program a PLC?
Programming a PLC involves using specialized software to create a control logic diagram, often in ladder logic format. This logic is then uploaded to the PLC, where it executes the programmed instructions in real-time. Some common programming languages for PLCs include Ladder Logic, Function Block Diagram (FBD), and Structured Text (ST).
Can PLC Systems Be Integrated with IoT?
Yes, modern PLC systems can be integrated with the Internet of Things (IoT) to enable remote monitoring and control, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making. This integration allows for real-time data collection and analysis, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Conclusion
PLC Control Systems have revolutionized industrial automation, enabling more complex and efficient processes while reducing operational costs. Their robust design and advanced capabilities ensure they remain a cornerstone in the field of industrial control systems.